Find experienced and well trained Hand Surgeons across the UK
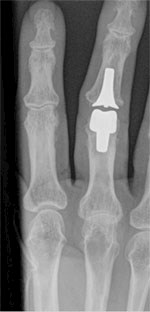
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Replacement (PIPR)
PIPR is indicated in both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. There are various types of implants that are currently used. They consist of either surface replacements (such as the Finsbury PIPR or the Acension Pyrocarbon PIPR) or silicone implants (such as the Neuflex or Swanson type).
The decision to use one type depends on a number of factors such as severity of disease, bone and soft tissue quality. The quality of the replacement and the outcome is often dependent on the degree of preoperative stiffness, deformity and stability. If a joint is very stiff pre-operatively it is unlikely that a good range of movement is expected post-operatively.
Therefore post-operatively rehabilitation is dependent on:
- Pre-operative deformity
- Post-operative stability
- Collateral ligament repair
- Quality of extensor mechanism
- Repair of extensor mechanism
- Intra-operative fracture
- Individual patient factors
Any or a combination of these factors may require an initial period of 3 weeks immobilisation followed by controlled/protected mobilisation dependant on individual circumstances. In the absence of these factors early mobilisation is the treatment of choice.
Method 1 - Early Remobilisation
Requirements:
Stable joint with good attachment of extensor mechanism, no collateral ligament repairs and no patient specific problems
Immediate post -op
Volar POP or bulky dressing to finger tips
Day 1
- Elevation
- Neurovascular observations
- Pain relief
- Antibiotics
Day2/4
- Reduce dressing
- Wound inspection and application of light dressing to facilitate movement
- Commence active mobilisation of joint
Method 1-for multiple fingers or excessive oedema
- Hand/wrist resting splint for all digits. Wrist neutral/20 degrees,MCP neutral, PIP flexed to 40 degrees
- This splint worn between exercise sessions and at night
- Hand based MCP joint blocking splint to direct movement to PIP joint, used during exercise
- Active flexion 10-20 repetitions hourly
- Discourage functional use of involved digits
Method 2- for single fingers
- Finger based dorsal PIP joint blocking splint with integral MCP. joint block. PIP joint positioned in 20/30 degrees flexion
- Active PIP joint flexion 10-20 repetitions hourly
- Resting splint (as method 1) at night
- Discourage functional use of digit
Week 3
Evaluate progress and record ROM
Extensor lag
- introduce extension assist splints and active extension to neutral
- in addition continue flexion exercises
- position PIP in extension during the night
Poor flexion
- introduce flexion assist splints
- continue active flexion
- position PIP joint in flexion during night
- encourage active extension to neutral
Monitor angulation of PIP and DIP joints and correct as necessary
Discourage power grip and deforming ADLs
Links: